Does “meaningful” short-term stock return momentum predict exploitable short-term price trends? In their October 2015 paper entitled “News Momentum”, Hao Jiang, Sophia Li and Hao Wang combine time-stamped firm news with high-frequency (15-minute) stock returns to identify stocks exhibiting news-driven momentum. Their news feed is the stream of unique items (no repeated stories) delivered in near real time by RavenPack. News-driven momentum derives from high-frequency returns that coincide with real-time news, arguably capturing the reactions of the most attentive investors. To test exploitability of news momentum, they each day form an equally weighted hedge portfolio that is long (short) the tenth, or decile, of stocks with the highest (lowest) prior-day news-driven momentum and hold for five trading days. On any given day, they calculate strategy return as the average return of the current five overlapping portfolios. Using intraday stock price/quote data, associated firm news and other stock/firm data for a broad sample of U.S. common stocks during March 2000 through October 2012, they find that:
- Gross near-term future stock returns increase systematically with daily news-driven momentum, increasing from -????0.78% per month for the loser decile to +2.55% for the winner decile.
- In contrast, returns not associated with news tend to reverse.
- The news-driven momentum hedge portfolio generates gross annualized average return 40.1%, translating to gross annualized Sharpe ratio 3.29 and gross annualized four-factor (market, size, book-to-market, momentum) alpha 40.4%.
- Results are generally robust to changes in methodology.
- The hedge strategy implemented with news-driven momentum measured via daily returns instead of high-frequency returns generates gross annualized average return 23.9% and gross annualized four-factor alpha 23.8%. In other words, high-frequency return measurement roughly doubles strategy performance
- The hedge strategy implemented after excluding earnings announcements from the news feed generates gross annualized average return 21.5% and gross annualized four-factor alpha 22.2%. In other words, earnings announcements account for nearly half of strategy performance.
- Unlike a conventional momentum strategy (monthly return skewness -0.79 and gross maximum drawdown 63.7%), the short-term news-driven momentum strategy is crash-resistant (monthly return skewness +0.51 and gross maximum drawdown 15.9%).
- Th news-driven momentum effect is elevated for overnight/weekend news, among small firms with less analyst coverage, high-volatility stocks and illiquid stocks.
The following chart, taken from the paper, shows gross cumulative gain for the short-term, news-driven momentum hedge strategy specified above for a $1 initial investment. Gross performance is largely consistent over time, with few drawdowns of modest magnitude.
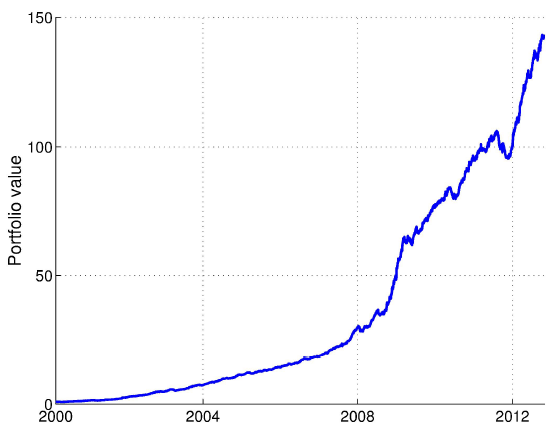
In summary, evidence indicates that a short-term momentum strategy focusing on high-frequency stock returns associated with firm news predicts near-term stock returns.
Cautions regarding findings include:
- Short-term, news-driven momentum strategy returns are gross, not net. Accounting for costs of implementation would substantially lower reported returns. Specifically:
- The corresponding author reports turnover of about 20% from day to day in forming overlapping portfolios.
- Gross profitability concentrates in relatively illiquid stocks.
- Shorting may be costly or infeasible for some loser stocks.
- The cost of high-frequency stock quotes and the RavenPack near-real time news feed (thousands of dollars per month?) would be material, even prohibitive, for many investors.
- High-frequency ranking of stocks according to the degree to which their returns are news-driven, and translation of this information into a daily portfolio over roughly the next 15 minutes implies a highly automated process. These tasks are beyond the capability of most investors, who would bear fees for delegating them.