How do stock index volatility and variance futures contracts compare with stock index put options as hedges against market crashes? In their August 2010 paper entitled “Using Volatility Instruments as Extreme Downside Hedges”, Bernard Lee and Yueh-Neng Lin investigate the effectiveness of stock index volatility and variance futures contracts as extreme downside hedges and compare this effectiveness to that of out-of-the-money index put options. Specifically, they compare the outcomes of hedging a long Standard & Poor’s Depository Receipts (SPY) position via 1-month and 3-month rolling positions in S&P 500 Volatility Index (VIX) futures contracts, S&P 500 3-month Variance Futures (VT) contracts and 10% out-of-the-money (OTM) S&P 500 Index put options with reasonable hedge trading frictions. Using price data for SPY, VIX and VT futures contracts and index put options spanning 6/10/04-10/14/09 for 1-month rolling hedges and 7/19/04-9/9/09 for 3-month rolling hedges, they find that:
- Rolling VIX and VT futures contracts are more cost-effective extreme downside hedges than rolling out-of-the-money S&P 500 Index put options.
- VIX futures are the most cost-effective choice for hedging extreme downside risk. And, rolling 3-month VIX futures contracts outperform rolling 1-month VIX futures contracts, indicating that the increased trading frictions of more frequent hedge adjustments outweigh incremental hedging value.
- Based on the relatively high liquidity of 3-month VIX futures contracts, real-life traders appear to have developed the correct market intuition.
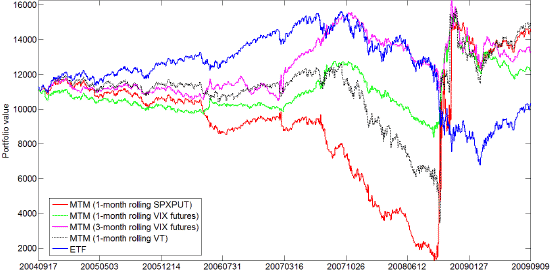
The following chart, taken from the paper, compares cumulative values (marked to market – MTM) over the test period of 100 shares of SPY that are:
- Unhedged (ETF).
- Completely hedged by 1-month rolling S&P 500 Index put options (SPXPUT).
- Completely hedged by 1-month rolling VIX futures contracts.
- Completely hedged by 3-month rolling VIX futures contracts.
- Completely hedged by 1-month rolling VT futures contracts.
The chart shows that hedging with 3-month rolling VIX futures contracts (1-month rolling index put options) is most (least) cost-effective.
In summary, evidence indicates that 3-month rolling VIX futures contracts may be the preferred way for investors to hedge stock market positions against crashes.